Contents
- 1 Let a pro handle the details
- 2 The Best SEO Tactics
- 3 Local SEO
- 4 White-hat SEO
- 5 What Works Today in Search
- 6 Embedding YouTube Videos
- 7 Duplicate Content
- 8 WordPress and SEO
- 9 How to do SEO on WordPress?
- 10 Content Relevance
- 11 Optimize Metadata
- 12 Reviews and SEO
- 13 Let a pro handle the details
- 14 Penalties
- 15 How to Rank in Google?
- 16 How Does Google Rank Pages?
- 17 High Competition Niche Top 10
- 18 Build Traffic to a New Website or Startup
- 19 SEO Mistakes
- 20 The Most Common SEO Services
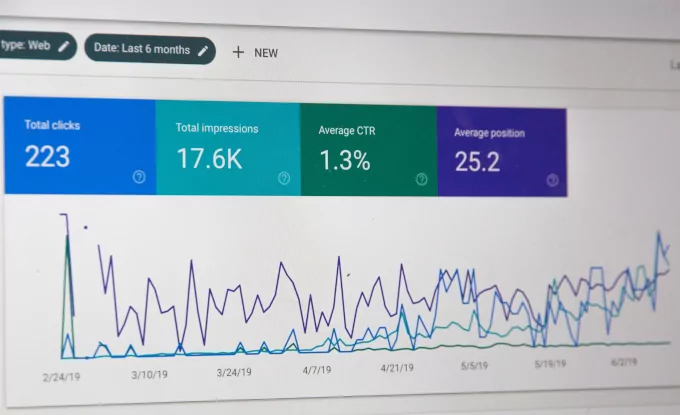
- 21 Key SEO Metrics
- 22 SEO Gigs
- 23 SEO KPIs
- 24 SEO for Large Enterprises
- 25 SEO Blockers
- 26 Pages That Don’t Rank
- 27 WordPress SEO
- 28 In-house SEO
- 29 Signals Google Want to See
- 30 Cheap SEO Services
- 31 Redirects
- 32 The Role of Sitemap
- 33 Navigation and SEO
- 34 Block Pages from Search Results
- 35 What Are Internal and External Links?
SEO is the strategy of optimizing a web page for search queries. Search engines discover content on the Internet and then rank it by relevancy to topics. When somebody searches for an answer, the results he finds in the engine are called organic, and if he clicks and visits a page, this traffic is called organic, natural, or free. Today, depending on the search query, you may encounter different results formats like videos, image carousels, video carousels, local pack (map), and Ask boxes. Many pages are in the Top 10 results because they have worked one way (SEO) or the other (rankings manipulation). Note that organic traffic exceeds all other traffic channels like social media, and paid ads, yet it costs less money than those, has lasting effects over time (retention), and attracts more clicks (paid ads in the USA attract less than 3%).
SEO is a marketing approach that focuses on improving online visibility. While the term is widely used, it is also commonly misunderstood. One of the most significant trends for organic SEO is the importance of advanced links. Advanced link-building strategies can increase your website’s Domain Authority (the score given to your site between 0 and 100) and thereby improve your overall visibility online. Advanced link-building goes beyond establishing generic directories, guest blogs, paid links, and web 2.0 blogs. Each of these strategies involves placing content on third-party sites with backlinks to your website, but some of them generate spam links. The more websites that point to yours with a substantial DA, the more visible your site will become.
fLet a pro handle the details
The Best SEO Tactics
✓ Secure your website with HTTPS (Google ranking factor). HTTPS encrypts information sent between the visitor and the server (the green lock icon on the address bar). You will need to install an SSL certificate on your server (the hosting can help you with SSL installation).
✓ Build a fast-loading website in under 2 seconds (Google ranking factor). Google nowadays uses the mobile index, so speed is paramount for the best user experience and low bounce rates. Content Delivery Networks (CDN), server cache modules, image compression, lazy-loading page elements, responsive templates, and cache plugins can boost the speed.
✓ Find low-competition keywords that match user intent. You need traffic today, and going for the high-competition keywords will take months or years. If you match the search intent by providing answers to less competitive queries, you will earn traffic in a relatively short time. Create content round-ups, lists, and any content that offers well-researched information on a topic. Write naturally thinking about what the reader wants not what the search engine needs.
✓ Create short descriptive URLs, offer content length above 1,000 words, and optimize your post titles and descriptions to earn clicks. Study your analytics, understand how people come and go, what works best, and stick to it. Plug a responsive theme and optimize your images to load fast on all device screens. Interlink your posts/pages without over-optimizing the link anchors.
Local SEO
Local, or map search, SEO has emerged as a distinct form of SEO over the last few years. On average 4 customers out of ten find local companies through maps. As such, strong map visibility is crucial. Instead of a website, local SEO requires that you optimize your Google My Business (GMB) profile with relevant text and links. Strategies for improving local SEO include NAP (name, address, phone number) consistency, link-building, image geotagging, and more features. Ensuring consistency and giving the appropriate time and energy to local listings is a critical factor in getting free traffic.
Local communities help a lot with local SEO. I will list some here; the Chamber of Commerce, local consultants, cultural groups, local events (sponsors), networking with local businesses, and local news. Note that the practice of trading links is a type of search engine manipulation (spam). Local news is an excellent source of backlinks for local SEO. You provide useful content, earn local exposure, and a link for your website that benefits local rankings.
Do you know that 46% of all searches in Google are with local intent? “Near Me” searches show 150% growth compared to traditional local-based searches; 74% of local searchers walk into the physical store on the same day of their search. Build some NAP citations, those online listings that offer fields with Name, Address, and Phone Number. Local directories are the best places to get NAP citations. Google My Business (GMB) is an excellent place to list your business as Google can verify your physical address.
Search engine results are based on personalization that also includes the user’s location down to the street level. A host of services are pulling the user location from all devices to personalize the content and ads they offer. It makes sense for a business that services customers in one or more areas to build relevant content (landing pages) embedding location factors like business details, opening hours, addresses, and maps of the physical store.
White-hat SEO
In principle (the way Google defines it), if you try to better the rankings of a website by doing anything more than optimizing on-page content, then you are manipulating the search engine results. White hat is more of a marketing term used by grey/black-hat SEOs or salespeople. Some SEOs are 100% white-hat but not efficient, meaning their rankings suck. If you run link-building campaigns, and content marketing targeting more inbound links, even if you are optimizing the page copy, you are at least grey-hat. So, again, in principle, every SEO out there is manipulating the rankings. The thing is what method you use that can produce results today without getting a penalty, as there are so many factors at play and changes that likely will override you in the future your current method. It would be best to stay sharp, adjust your plan following the changes, and always produce results, that’s my approach.
What Works Today in Search
Videos will continue to appear in the search results and drive more traffic. It’s time to formulate a video SEO strategy while YouTube remains free and is owned by Google; hence its videos show up in search results. Choosing the topic or type of video does not require much effort and directly depends on your niche and your offer. Many niches on YouTube are not saturated yet, so there’s plenty of room to exploit this free traffic source and the second-largest search engine. Rich snippets are also a thing together with voice search, so a modern business should research and optimize the various schema types.
Embedding YouTube Videos
It will help by increasing the time-on-page, provided the videos have some value for the visitor. It could work with any video hosted on your site, embedded from YouTube or other video sites. Directly affecting page rankings, no, it won’t help. So you have to factor in, if it is worth your time to insert and maintain those videos, as some tend to drop from YT (getting deleted or changed to unlisted/private), and weigh in if you can achieve a better UX in other ways. It’s not a given that visitors will click to watch the videos just because they are on the page.
Duplicate Content
It will affect a small percentage of the quality of all pages sharing the same chunk of text. It won’t matter for a couple of pages, but if you replicate it on all existing posts or will do that shortly, the minor issue will grow. I’d suggest you devise ways that relate to the crawlability of the disclaimer, e.g. insert it as an image or render it with a script (but images don’t require technical skills or plugins).
WordPress and SEO
WordPress is the best CMS for SEO. It combines SEO-friendly features, modern coding, plugins, super user experience, and speed. A large community of programmers secures its development, and webmasters seem to like it a lot with millions of installs. After plain HTML, I put it second best in SEO performance. It is fit for professionals and amateurs and can host blogs, small e-shops, affiliate landing pages, and more. Let’s look at its SEO features now:
Permalinks make the URLs SEO-friendly allowing the insertion of keywords. Metadata and images are easy to handle right from the first minutes of installation or allow more room for tweaking with the help of plugins like Yoast SEO. Cache plugins make WP load like a breeze lowering time to load, so fundamental for better Google rankings. A host of mobile-friendly themes help WP rank in the established Google Mobile Index. WordPress pings the search engines each time you publish new content. WP is easy to integrate with a host of analytic tools. Lastly, you can raise the level of security with its powerful plugins avoiding DDOS attacks, unauthorized logins, code insertion, and more.
How to do SEO on WordPress?
Wordpress is one of the best web scripts when it comes to being SEO-friendly. Start with Wordpress security. Install an SSL Certificate, which gives a slight boost to SEO. You need to have a safe website, and Google likes to list secure websites in its search results. Hosting companies offer free SSL for the first year, or you may use the Free SSL service, Let’s Encrypt.
Then you need to make sure you have SEO-friendly URLs. You can make the change to ‘Post name’ from the Settings / Permalinks WP page. There are more steps to follow and require an amount of work, but there is a plugin that can save you some time. Go ahead and install the Yoast SEO Plugin that allows you to connect your WP with Google Search Console. Yoast is a must-have SEO plugin. It prepares automated sitemaps, offers title and meta fields to optimize for each post/page, gives you recommendations when problems occur, manages taxonomies, etc. Now that we have covered the basics, you can publish your posts, keep the titles relatively short, fill in all meta fields, and do not forget to optimize your images with ALT tags.
Content Relevance
Google tries to understand the page content and natural language better. The goal is to offer the best answers to people using the engine and benefit from its paid program (Google Ads). The BERT algorithm focuses on content relevance by assessing the context of words in searches and matching those queries with HQ results. BERT is a natural language processing NLP framework trained on Wikipedia and tweaked with questions and answers datasets. BERT changes the way Google interprets queries because people are using longer, natural, and complex questioning queries. It will benefit international SEO when the datasets are ready to run in the algorithm. We are way past the artificial copy used in SEO to game the rankings. To recap, creating content in natural language, not focusing on keywords in a text that doesn’t make sense, and writing in the current language of the targeted country, are best practices.
Optimize Metadata
I recommend inserting your main keyword in the title, the Meta Description, and the H1 heading. The other headings below h1 can use a variation of the keyword in a way that makes sense for the reader. Click-through rate (CTR) is a significant signal to Google. All the metadata above should use natural language with the intent to attract clicks, not manipulate the search rankings. If you don’t have the best title and description, nobody will visit your page regardless of its rank. And even if you’re #1, but your page copy reads as unnatural, you won’t be for long as you’ll have many drop-offs, and high bounce rates, and Google will demote your page. So, CTR plays a significant role in ranking a page. If you are on the first page, it is possible to take the place of the first website just because people prefer your page (given that they bounce from your competitors and stay longer on your page as more relevant to their search queries). I recommend you optimize your titles and descriptions; the latter should show up entirely on the search page and not cut off. Experiment with different sets of titles and descriptions to see what works best.
Reviews and SEO
My take is that they don’t help and never have. Initially, people expected that review snippets were ranking signals. It proved that it wasn’t, and I also doubt if people see the stars and click on the search results with five stars. Of course, it attracts the eye but other than that, I believe only the titles and description can influence the click-through rate. Reviews offered a helping hand to legitimate businesses and ended up abused and rigged. Trustpilot built a whole business around it, and it costs a lot of money to get in without any tangible benefit. For the rest, people started building fake star reviews (schema spam), and most reviews from real people are, in large part, incentivized. For all the above reasons, I’m sure Google will take them down sooner or later. I don’t see any point in a business working hard on getting reviews. If the customers like to leave an honest review, they are free to visit the GMB page and leave it there for as good as it is. Don’t sweat about getting reviews; it’s not worth it.
Let a pro handle the details
Penalties
There are two types of Google penalties, automatic and manual action. If the webmasters are amateurs in SEO (a fact in the majority of cases), they will never have a clue and may never recover from an automatic penalty. That said, the hit came because the webmaster did not comply with the Google guidelines. In the case of the manual action, the webmaster gets a message in Google Search Console that he has violated Google’s Terms of Service. This time the webmaster has done something intentionally, and has a hint of what to fix as the message doesn’t give any instructions. The cause of the manual action could be a redirect that went wrong, schema portraying false data about the page, i.e., showing fake five stars reviews, buying/selling/exchanging links (link schemes), doorway pages, malicious behavior (active or passive, i.e., hacked site), thin content, keyword stuffing, hiding text, etc.
First, do your research. Do you find any pages losing rankings abruptly or disappearing from the index without you changing anything? Have you checked the Search Console for any messages indicating a manual action taken from Google? Have you bought any SEO gigs recently? Backlinks, blog comments, forum profiles, bookmarks, guest posts, exchanged any links? All the above in large quantities can trigger an automatic penalty. Have you changed your website content or sold any links from your articles? If none of the above, then something’s changed in the engine, and you’ve been affected. The best thing to do is go through the recent Google updates for any hints or seek professional help. It’s not a matter to neglect as it may never go away and you can’t afford to lose business.
How to Rank in Google?
When you don’t see all your product pages in the Google index or the new pages you have built, then you have indexation issues. Dynamic content or site search results don’t work. Problematic navigation and many filters confuse search engine crawlers. You might have an infinite loop, pages directing to a series of other pages without end. Suggestion: Trim as much as you can the parameters (session ID, filters, etc.) in the URLs as they generate issues for the search engines. Block them via robots.txt. Restrict product filters to an absolute minimum. Avoid using query parameters or use the Google Search Console to filter them out. Use canonical tags for each page. I avoid working with a website that appends parameters in the URLs because search engines will have to deal with an infinite number of copies of the page I try to rank. The developers didn’t think there would be a need to do SEO when they designed the shop. Inert internal links, broken links as we call them. You might have changed something or a middle page got deleted or unpublished for some reason. Suggestion: Run an audit. There are desktop programs like Xenu (free software) that scan your website and identify broken links. You might as well try to use one of the numerous online tools to look for broken links.
How Does Google Rank Pages?
Google looks out for in-depth and useful content written by experts. The policy prevents people from creating content on topics outside their area of expertise, as it could be traffic manipulation or cause problems for people looking for answers and help. With topic clusters (that show content depth), the content creators present their expertise on the topic. The coverage of content reassures the search engines that the writer knows very well the subject. It’s a misrepresentation at times because even experts make mistakes, and quantity does not equal quality. Plus, the search engines would need an expert on every topic to assess what the website expert says, which is not practical.
High Competition Niche Top 10
Given that the niche is top competitive and not considering any blog posts currently ranking but pages ranking with money keywords, an average domain will require at least three years. During this time, it should be able to present top metrics in user engagement, quality traffic, content relevance, metadata optimization, etc. With articles, it can take 1 to 6 months, to show some (not all) of the above quality metrics. But to maintain the top 10 positions will eventually have to meet all quality criteria too.
Build Traffic to a New Website or Startup
Work on preparing posts on trending topics. If you have a brand new website, you can’t beat other people’s evergreen content. For new websites, it is the best opportunity to rank fast because the topic is not saturated. Google has an algorithm on content that’s fresh (trending) that “…impacts roughly 35 percent of searches and better determines when to give you more up-to-date, relevant results for these varying degrees of freshness.” Fresh content doesn’t mean new but trending and relevant to the search query.
Don’t change your content to make it fresh. You can update it if it makes sense (correcting facts, adopting a modern approach), but changing it for the sake of rankings, won’t give it a boost, rather the opposite. Make it relevant or build more content that’s relevant to what people seek today. Trending content is a reliable traffic source to make an entrance, but you will also need evergreen content to keep the visitors coming back.
SEO Mistakes
✓ Duplicate content is a significant problem. There’s a penalty named Google Panda that penalizes sites with content quality problems. Among the causes could be poor or scraped web page copy, thin content, duplicate titles, meta descriptions, and headings. I’ve handled cases like the one when I was working on a landing page with the owner having built unbeknownst to me 2,000+ pages with similar content, titles, and descriptions to my target page.
Duplicate content is an SEO trap; throttles organic performance; reduces page indexation; and demotes the duplicate pages or the whole site if it’s a widespread problem like the one above. Canonical tags and backlinks can’t save the day. I was creating content, and building backlinks only to discover an enemy within. The fix is a technical SEO audit, difficult and costly. The owner wouldn’t consider spending money on doing a professional job, so he tried to correct things by himself. I gave him a couple of guidelines, but the audit needs to be thorough and run with an expert eye. Needless to say, after weeks of him changing pages there was no progress.
✓ Automatically generated content when you copy and paste content found on the internet without curating it, or you have software that generates articles that you upload on your page. Another case is when you have an auto-translation widget on your site that translates content from your original, natural language to whatever the result in the target language.
✓ Participating in link schemes when you buy or sell links. You could be exchanging links with other pages, building a private blog network (PBN), selling links from within your articles (contextual), or sitewide (sidebar, footer). The same stands when buying links from external web pages (everywhere an incentive is found).
✓ When you create thin content; pages that have no value and no reason to rank, or you wish they would rank but don’t invest time to put some quality on them.
✓ When you misrepresent your business information, create fake addresses, and PO boxes; You abuse the positive reviews on and off-site like the Google My Business listing, Amazon reviews, Trustpilot, Android Store, etc.; you buy links to raise the authority of your pages, and even worse you use online forums, i.e., Fiverr.com, Freelancer.com, Upwork.com, Thehoth.com, etc., that sell cheap backlinks not fit to your website needs.
✓ When you build a page for each location (wishful thinking) even though you don’t have the right amount of original content that meets the local needs; you are not optimizing for your local area first which would make sense given the fact that you are on a budget; you target with a separate page every keyword phrase you find in online tools.
✓ When you are trying to compete with a slow website, especially on mobile devices, that creates a bad user experience; you serve pages on insecure HTTP protocol regardless of the Google guidelines to offer HTTPS, so you are missing a slight ranking boost and never make it to the first page; you build your URLs with dynamic parameters that search engines cannot follow and create duplicate content issues; you build a page for each keyword phrase that looks shiny in online research tools.
✓ When you abuse your link profile trying to inflate the number of backlinks. Google can take out your pages from its index.
✓ Here are a few grave mistakes you can intentionally make: Showing different content to search engines than your visitors to game your rankings (that’s cloaking, a black-hat tactic). Related to Cloaking is when you hide text and links again for higher ranking purposes, for example, you color the text with the same background color and you hide the links behind images or other elements. Another black-hat scheme is the doorway pages, which aim to occupy high positions but then redirect the visitors to the content they would not expect to find when they run the search. It is a common scheme mainly for unethical advertising purposes.
✓ Here are some intentional but not-so-grave mistakes: Creating bigger titles and descriptions than the average competitor has and stuffing keywords in them; Manipulating traffic by buying social signals (likes, tweets, shares, comments); Over-optimizing page content, schema markup, and image alt tags; Manipulating schema markup to show features you don’t have, i.e., five-star ratings; creating thin content only for affiliate purposes; redirecting visitors to other properties or redirecting old domains with irrelevant content to your pages.
The Most Common SEO Services
Technical SEO deals with all setup and performance matters from website coding to crawling, indexing, website speed, content auditing, and fixing issues. Technical SEO is crucial for the performance of the organic channel. A website that’s lagging has redirect issues, or poor content and navigation structure will have many drop-offs (high bounce rate) and never get significant traffic.
On-page SEO is about optimizing metadata from titles and descriptions to images and internal links. It all starts with competition and keyword research, then passes to mapping keywords to landing pages, and lastly, optimizes on-page content. On-site SEO is also about performance, so it measures traffic and conversions from organic traffic. Researching and creating content that responds to search queries is crucial to getting more traffic.
Off-page SEO seeks to lead generation better and achieve higher rankings in the search results. It’s about creating content published off-site, increasing brand awareness (mentions), and advertising the website offers. Of course, link building is fundamental to off-page efforts and intrinsic is the need to monitor the quality of backlinks to avoid search spam and negative SEO (spammers, competitors trying to destroy SEO performance).
Local SEO is about optimizing brand listings in local search results (Google Maps, mobile devices, ‘Near me’ results). Professionals give extra attention to customers finding them online around their area. Research shows that 72% of consumers who did a local search visited a store within five miles. I do the same, and I bet most of you are reading this do the same.
Video SEO is about optimizing videos for YouTube search results. Video SEO is not as saturated as Google SEO is, and there are many opportunities to rank videos in national or local results. I offer this service with a brilliant method that delivers awesome results to my clients.
Key SEO Metrics
The old PageRank, Trust flow, Domain authority, and Citation Flow don’t mean so much anymore.
Why? Because they don’t put a page on the Top 10. What does? Clicks and low bounce rates mean that the page has interesting content and people stop to read it. Even sharing interesting content doesn’t mean much to me apart from traffic.
Take a page that has new content and gets a lot of shares. It will see a traffic spike, and Google will probably rank it higher for a couple of weeks if the page story is good enough. That’s trending content. What happens next? The page will compete with those pages that have evergreen content and occupy high positions in search. Then the page will tank like the rest of them. Bottom line: don’t look at the metrics. See if you can create evergreen content and the metrics will come in their own time.
SEO Gigs
Let’s take for example the following Fiverr gig: it costs $5 offering Page Trust Flow 10+, Page Citation Flow 10+, and Domain Authority 20+. Unlimited URLs and KEYWORDS accepted. All links are 100% Dofollow. High Trust Flow and Citation Flow. All comments stay on the actual page. Manually submission. 100% Satisfaction Guaranteed. I will deliver my service as promised. Delivery is Always On Time. Plus 24/7 Support. Detailed Excel Report.
Here is my take. It says all comments stay on the page which means he’s doing blog comments. I doubt the 300 links are all dofollow since they come from blogs. Domain authority 10+ despite saying below that he offers high trust flow; that’s very bad. Such low authority creates spammy backlinks. Citation flow 10+ despite saying below he’s offering high citation flow. If he knew what he was talking about, he should emphasize the low citation which means the sources have low backlinks, but he doesn’t know the sport that’s why he’s stressing the high citation metric. I also doubt the manual submission, there are 300 backlinks promised and he would need more than a week to deliver. One week working for five bucks isn’t worth the manual work in any depreciated location on earth. So, he’s using automated software to blast the blog comments. Lastly, 24/7 support is a joke. The gig is spam and will get you into trouble. Blasting low-quality backlinks you can’t expect your pages to go up; the contrary will happen.
SEO KPIs
Sessions (visits), page sessions, impressions, keyword positions on the first page, CTR based on estimated position, revenue (current revenue per visit), campaign outreach referrals, conversions, direct traffic (SEO contributes to it over time with brand mentions).
Opportunities: discovery optimization (anticipating user intent), answer box positions, embedding Google Ads’ best-performing keywords into organic campaigns, optimizing Google Ads against click fraud.
SEO for Large Enterprises
Setting the correct KPIs is a key step that you will find in all future interactions with the company stakeholders. Management and digital marketers are not experts in SEO, so you need to break it down to them and make sense of it all. After all, you need these people to approve your budget and act on your suggestions if they don’t adopt the organic channel every action you take will fail. Who are the stakeholders? Digital marketers who own the landing pages, web engineers, the management, and possibly one or more external agencies. Different groups with low to zero understanding of how SEO works and what it can bring; are always focused on revenue and easy solutions like paid advertising which costs them a fortune to run compared to organic.
Set reasonable goals for the KPIs, expect all kinds of issues ahead that will delay or block organic performance, and hope for the best. If you manage external agencies, you need to be the corporation rottweiler, so they don’t spam the company website, and they provide some growth for the huge amount of money you spend. With web engineers, make sure they understand that there are no second thoughts or alternatives to what you need and no time to lose. Otherwise, they will bring up all kinds of excuses why this won’t work or why they can’t do it now or in one year. Also, make sure they understand the need to keep you in the loop for upcoming changes, releases, domain transitions, and other ingenious stuff they devise to keep their salaries running.
SEO Blockers
You may have crawling and indexation issues. Google sends its bot to read your pages and then computes several factors, including technical parameters on the server and website, metadata, page content, relevancy to the topic, etc. If you have a problem, you can visit Google Search Console and check any error messages in the tab Sitemaps or if there are any pages with errors in the tab Coverage. You may block crawling the page in your robots.txt file, or you have a Noindex tag on the page. Remove the Noindex tag from the page and its reference from your robots.txt file. You may let Googlebot repass on the page or submit the change to the tab URL Inspection. Check also if the crawler can find your page or reports a DNS or 404 error. If you still don’t see the page indexed, then you need an expert to run an audit and identify the issues. Problems like those won’t ever go away, and you will be losing business not fixing them. I see business owners still struggling because they wanted to save money and didn’t follow my suggestion of fixing the issues.
Pages That Don’t Rank
You may have a slow website, so Google sees that you don’t pass this ranking requirement. Websites, regardless of their setup, desktop or mobile, should load in two seconds else the user experience is bad. Mobile speed optimization is a must as Google focuses on mobile devices. What that means is that they will probably bounce, and you’ve lost them forever. Google has the Chrome browser and Google Analytics installed, plus other services to see whether you can attract clicks and keep the visitors engaged with a fast-loading website and interesting content. If you don’t there’s no point in ranking high, is there? Google has introduced the AMP feature to help webmasters build faster websites, plus it provides a speed measuring tool with its tool PageSpeed Insights.
Slower pages are all about bad user experience, meaning if visitors stay, they don’t convert well, they don’t buy, don’t subscribe, don’t revisit. On the technical side, they are not friendly to search engine crawlers, which might report errors and not index slow pages. Start with the PageSpeed Insights and work your way into optimizing both website versions.
WordPress SEO
WordPress in one of the best when it comes to being SEO-friendly. Start with WordPress security. Install an SSL Certificate, which gives a slight boost to SEO. You need to have a safe website, and Google likes to list secure websites in its search results. Hosting companies offer free SSL for the first year, or you may use the Free SSL service, Let’s Encrypt.
Then you need to make sure you have SEO-friendly URLs. You can make the change to ‘Post name’ from the Settings / Permalinks WP page. There are more steps to follow and require an amount of work, but there is a plugin that can save you some time. Go ahead and install the Yoast SEO Plugin that allows you to connect your WP with Google Search Console. Yoast is a must-have SEO plugin. It prepares automated sitemaps, offers title and meta fields to optimize for each post/page, gives you recommendations when problems occur, manages taxonomies, etc. Now that we have covered the basics, you can publish your posts, keep the titles relatively short, fill in all meta fields, and do not forget to optimize your images with ALT tags.
In-house SEO
First, you need to make sure your site is accessible to search engines. I mean from the technical side all content, pages, metadata can be crawled and indexed from the search bots. Then you need enough high-quality content that can answer the niche search queries adequately and even predict user intent. The next step is to optimize the content to surface on the search engine’s first page which is good enough to attract clicks. Here I should mention the need to embed schema markup that will enhance the relevancy of the page. Don’t forget to optimize the user experience during their visit with a fast-loading website suitable for all devices and great design with strategically placed conversion elements.
Signals Google Want to See
Google has some rules (webmaster guidelines) that would like everyone to abide by. They have help forums and host live office-hour hangouts for webmasters. Google guidelines are relatively easy to follow. You design pages and create content for the visitors; you follow a set of rules published on Google help forums, and ideally, you have no problems. In reality, you bump into a lot of issues unbeknownst to you as you start with good intentions, but pretty soon you discover that things don’t work as Google says they do. So, you don’t see your content getting any first-page positions or clicks, your website gets unnecessary visits and bots, and the money you spent building it, brings you zero return. I am sure you have understood that there are limitations to what you can do, and the cheap services you buy are worth nothing. You need an expert to start things rolling.
Cheap SEO Services
Of course, you do. You get all sorts of negative results that tank your traffic, maybe forever. It’s strange to spend money destroying your business page, but most people do. People like to save money, don’t they? Why pay hundreds or thousands of dollars to people with 10+ years in SEO when you can do it for a couple of dozen bucks buying a gig? After all, everybody says they are experts, and all promise to get you to the first page. Buying cheap SEO services is the most common theme in our industry, and it’s been going on for years. Business owners get burned every day, chasing the first-page dream. Scammers have no moral boundaries. They promise to get them on the first page with unlimited keywords in 30 days for all-in-all $200 with white-hat SEO. That makes sense, right? So, what have they got to lose besides a couple of hundred bucks? Well, they will lose their organic traffic with no fixing, is that a small loss?
Redirects
The only SEO-friendly redirect is the 301 (permanent) redirect, and webmasters should implement the 301 redirects on any page that is not under development. Old content should be redirected to the updated version if it sits, points to a sitemap page with navigation links, or to the homepage. As a last resort, it should point to a 404 page (Google does not like 404 errors). Note that with a 301 redirect, you can retain the link equity (transfer page authority) to the new destination. If there is no redirect, the link equity is gone, and eventually, the page drops from the Google index. The 301 redirects should be done from page A to page B. Redirect chains of more than two pages (A to B to C) are bad for SEO as it looks like a spammer hides the real content and misleads visitors and search engines. 302 redirects are only viewed as a temporary solution when in development and not designed for content that needs to rank (bad for SEO).
Domain 301 redirects sit in the grey-hat SEO area. They may be beneficial for a while, but in the long term, they will lose the link equity they pass and possibly harm the receiving domain or page. If the old domain has different content than the receiving page, it will have the above negative effects for both. Do not waste money in buying expensive, high-authority domains only to redirect them.
The Role of Sitemap
Googlebot uses the sitemap files (page sitemap and sitemap.xml) to discover content.
The pages discovered go into the ranking algorithm and then get their positions in the search results. It is fundamental to offer at least the XML file as a map to content discovery. Google Search Console has a tab where you can submit it, and Googlebot will prioritize the crawling of pages. In the sitemap file, you need to include only those pages you want to show up in the search results, and you may add more information like alternate URLs for the languages present on the site. When Googlebot crawls a list of prioritized URLs on a site (because it runs on limited resources), it may encounter errors. Sometimes, there are also old URLs in the Sitemap that don’t exist anymore. Bad navigation, lack of interlinking, server errors, sitemap false page reporting, all those things may confuse Googlebot and assign a low crawling priority to the site. There are online tools that help with each error from lost links, missing pages, excessive redirect chains or loops, and of course, Google offers the Search Console with some reports that help webmasters identify the mishaps.
Google has four ways to discover your content.
i) Crawling with their bots,
ii) the Sitemap file,
iii) direct submissions you do via the URL Inspection option in Search Console, and
iv) users visiting pages through the Chrome browser.
There are more ways we suspect they use, but that is not the scope of this bit. When a bot crawls the site, navigation and links are the ones to indicate there is more content to discover. They show the path guiding the Googlebot from page to page. Pages not linked in any way may never be found, this I call buried content. It is a white-hat way to hide your content from the search engines 😉 Common mistakes are: Menus realized in Javascript that hide navigation links, different menus on mobile and desktop, serving personalized navigation to users, lack of navigation hierarchy that bots can follow; and lack of a sitemap page (different from the XML file).
Block Pages from Search Results
You have three options: 1. You could block the page from being crawled in Robots.txt with a ‘disallow’ command to Googlebot and other bots (User-agent: name-of-bot Disallow: private-URL). It does not mean that all bots will follow the instructions, Googlebot will do so, but most of the others will ignore it. Since everyone is using Google to search, it will work. Some bots target specifically hidden or private content, so putting the command in Robots.txt gives them a hint of where to find your private pages. The file is also available to anyone typing its path (domain.com/robots.txt) so take note before disclosing private content there.
2. You can insert a noindex tag in the page header. If you don’t want to give the bots a hint where to find your content, use the noindex tag only, don’t put anything into robots.txt. No guarantees that your content will remain private though, except for Google which is the thing most people care about.
3. If the page is already indexed, you can submit a request to Google to ‘temporarily’ hide the page from the results (Google Search Console / Removals), and it will work immediately. No worries about the ‘temporarily’ property, it will remain hidden from Google if you use the robots.txt command or a noindex tag.
What Are Internal and External Links?
It’s good to have a mix. You build internal links when you connect pages from the same website together (interlinking). It is always best practice when you interlink pages that talk about the same topic.
When you give a link to a page outside your website for any reason, this is an external link. Usually, blogs give external backlinks to other sites from their sidebar and their footer sections (these are sitewide links and search engines don’t give them much credit). When you insert links in the body of an article, this is an editorial link and passes the most link juice because the writer considered it of high-value to the readers.
Take care with external links; the quantity matters so much; if you give more than 20 from a page that has only a few paragraphs, Google sees it as a low-quality page. If you extend the practice to other pages of your site, again from pages with poor content, Google might think you are building a link farm (spam).