Contents
- 1 Hidden Text
- 2
- 3 Keyword Stuffing
- 4 Let a pro handle the details
- 5
- 6 Doorway Pages
- 7
- 8 Scraped Content
- 9 Sneaky Redirects
- 10 Automatically Generated Content
- 11
- 12 Article Spinning – Duplicate Content
- 13
- 14 Link schemes
- 15
- 16 Link Exchanges
- 17
- 18 Over-optimization
- 19 Guest Posting
- 20 User-generated spam
- 21 Let a pro handle the details
- 22 Cloaking
- 23 Bait and Switch
- 24 Referrer Spam
- 25 Pinging
- 26 Trackbacks
- 27 Link Directories
- 28 Social Bookmarking
- 29 Press Releases
- 30 Whois databases
- 31 Article Directories
- 32 Reviews
- 33 Paid Advertorials
- 34 Pages with Malicious Behavior
- 35 Parasite Hosting
- 36 Private Blog Networks (PBN)
- 37 Google Bombing
- 38 Negative SEO
- 39 Thin Affiliates
- 40 Rich Snippet Markup
- 41 Let a pro handle the details
- 42 Widgets
- 43 Toxic Sites – Bad Neighborhood
- 44 Blog Reviews
- 45 Automated Google Queries?
- 46 Wikis/.EDU Domains/.GOV Domains/Wikipedia Hijacking
- 47 Cybersquatting – Domain Squatting
- 48 Domain – Page Hijacking
- 49 Buying Likes and Followers
- 50 Mirror sites
- 51 Traffic Boosters
- 52 Microworkers
- 53 Fake Video Views
- 54 Cookie Stuffing – Dropping
- 55 Email Marketing
- 56 Mass Search Engine Submission
- 57 Fake Awards (Nettyawards.com and Thenettyawards.com)
- 58 How to Fight the Fake Awards Scheme
- 59 How to Fight Comment Spam
- 60 How to Report Spam
- 61 Let a pro handle the details
Note: The video contains only 26 tactics.
You can read all the 48 tactics in the article below the video.
48 Black-hat SEO tactics, what software and online services spammers use, what are the ways to protect your site
Black-hat SEO is a term used for specific techniques in the SEO industry deemed sinister against other parties or the same actor.
Hidden Text
It’s an old technique from when people used to hide links and text to achieve better rankings in Google. Spammers used to set the font size to 0 or something above 0, use the same color font as the background i.e., white text on a white background, position text off-screen with CSS, locate text behind an image, or hide links by linking one little character.
Google soon discovered the gimmick and hit hard all the spammers. There is a section in Google Search Console Help about Hidden Text and Links where it says: “Hiding text or links in your content to manipulate Google’s search rankings can be seen as deceptive and is a violation of Google’s Webmaster Guidelines.” Source: https://support.google.com/webmasters/answer/66353.
When using a text-based browser like Lynx, you can see what Google bot crawls. As a general rule, anything that’s not viewable is spammy. Remove anything that raises questions about its legitimacy or use to human readers. All tricks come to light and become useless and spammy.
Are people still using the technique today?
Yes, there are a few.
What happens to them?
They get eventually caught and penalized, but even before that, their pages don’t get any push as the spammy tactics don’t work anymore.
Google does not penalize the accessibility elements. Pictures, Videos, JavaScript, and Flash, should offer some descriptive text so disabled people and search bots can understand what the item is about. For images, you can use descriptive text in the alt=”” attribute. For Javascript place the exact content of the Javascript element in a noscript tag. For videos offer descriptive text in HTML or even publish the transcripts.
How to fix the Hidden Text issue?
Offer all content and links in regular size and color, clearly visible on-page. Use the alt=”” tags for images. Place the exact content of the Javascript in a noscript tag. Offer descriptions for videos or transcripts.
Keyword Stuffing
Keyword Stuffing and Keyword Density are closely related. Keyword Stuffing refers to the gimmick of spammers loading webpages with keywords to game rankings. The keywords appear unnatural, repetitive, and out of context. It’s an outdated technique that falls into the over-optimization bucket. Keyword stuffing is a bad user experience and offers no value to a human reader. Examples of this tactic are lists of cities, states, and phone numbers without any benefit to the visitor. Google introduced a penalty trigger in its algorithms under some form of Keyword Density. They call it Irrelevant Keywords – which represents a percentage of repetitive keyword phrases one tries to rank with to the total text on the page. A higher density rate raises a red flag, and the page has no luck in ranking as it is low-quality content.
How to fix the Keyword Stuffing issue?
Don’t write your content around keywords but on topics. Keywords don’t work the same way as in the past. It’s the topic relevancy that matters now, not keyword percentages.
Let a pro handle the details
Doorway Pages
A Doorway Page is a cheating tactic. Scammers built doorway pages or domain names to game the rankings essentially tricking users with many similar search results to go to the same destination page with redirects. At times, it’s not 1 to 1 page, as there can be more intermittent pages (see below the section Sneaky Redirects on the way to the destination to generate affiliate pageviews (unnatural traffic) or ad revenue. All doorway pages cloak the end page, and in cases where they have the same destination, they look similar in design and content. Doorway pages send users to irrelevant content contrary to their search queries. Note that more than two redirects are not good practice for ranking a page. Google tackled the doorway pages issue with a penalty in 2015.
Another way of generating traffic is when a phone user (the recent case with the iPhone exploit exposed by Google Project Zero) visits a hacked site then his/her phone gets attacked by an exploit, and if successful, installs malicious software. The hack accesses users’ apps including Instagram, WhatsApp, and Gmail to gather users’ images, contacts, passwords, and other sensitive information from the iOS.
How to fix the Doorway Page issue?
- Offer the same content on-page as the search results suggest.
- Remove all intermittent pages and redirects.
Scraped Content
Spammers, some affiliate marketers, and shady content curators steal “scrape” original content from websites that spend resources on writing content. The aim is to have enough content to attract visitors and game the rankings regardless of the uniqueness of that content. Apart from copyright infringement, and illegal practice in many countries, scraping content that is already indexed in Google, offers no real value. Even modifying the content using automated techniques is a no-go. Copyscape.com is an online tool that helps with scraping issues and also identifies the originality of produced content.
Software used: SEnuke TNG, GSA Search Engine Ranker, ScrapeBox, AutoblogSamurai.
Online services: Article Builder, The Leading Articles, Kontent Machine, Article Forge.
How to fix the Scraped Content issue?
Produce only genuine content. If you scrape content, you are a spammer and risk being confronted with lawsuits.
Sneaky Redirects
There are useful redirects i.e., when you redirect traffic from an old deleted page to a page with relevant content, or when you move the domain and its content. Sneaky redirects are those built to deceive search engines and visitors. The practice is deceptive because the crawled page that shows up in search has nothing to do with the destination page. Another form of sneaky redirect is when desktop users see normal content but mobile users see an irrelevant spam domain.
How to fix the Sneaky Redirects?
Use 301 redirects only to direct visitors from your old content to its new location.
Automatically Generated Content
There are software and AI apps that can generate automatically content without any human intervention. You simply run the program or log into a web interface, enter a couple of keywords, and it takes a few seconds to have your article ready (generated programmatically). The aim is to have a readable piece in your niche, with a few dollars, ASAP so you can build a website in a couple of hours and wait for it to rank. A closely related technique was pulling articles from any online or offline source and spinning them (modified with synonyms with article spinners) into a new piece of content. It used to work in the past. Thousands of affiliate websites with automated content were born and got a portion of the traffic pie until Google struck them with the Panda penalty.
Automated content has many drawbacks. It is marginally readable; It lacks writing style; Has no curator, no spacing, or alignment; Stands out as unnatural, and artificial. Scraping RSS feeds or directly copy-pasting content from web pages offers no value. Google is very proficient in detecting artificially generated content. You may see a significant traffic drop or even your website drop off the search results.
Software used: SEnuke TNG, GSA Search Engine Ranker, Xrumer, AutoblogSamurai, FB Autoposter 24×7, Viral Autobots, Octosuite, Social Traffic System, Social Auto Poster, Content Professor.
Online services: Article Builder.net, The Leading Articles, Kontent Machine, Article Forge, Uawpro.com, Rssmixer.com, Rssmix.com.
How to fix the Automatically Generated Content issue?
Use human content writers. Don’t use automated software; don’t drip-feed the content. It makes no difference for rankings, and you are producing spam.
Article Spinning – Duplicate Content
Since I’ve talked above about automated content, I will briefly touch on Article Spinning, which came as a means of avoiding the issue of Duplicate content.
Duplicate Content
For those who haven’t heard about Duplicate content, here is how I define it. Two or more pages, either on the same site or on different websites, share exactly or in large part the same content (text, paragraph split, meta fields, even images). The content was copied (see scraped content definition above) from the source and multiplied in one or more places online. For search engines, this is a big problem as they try to assess the quality of online content and rank the best of it. There were instances where scraped/duplicate content could rank better than its original publisher. Google introduced an internal way to measure page quality and penalized duplicate content pages/sites with the Panda penalty. Note that Panda is looking at more signals that determine page content quality, but it is useful to keep in mind that the Panda algorithm requires no curator. It’s automated meaning the bots crawl millions of pages, and the algorithm compares, ranks, and hits with demotion the problematic ones.
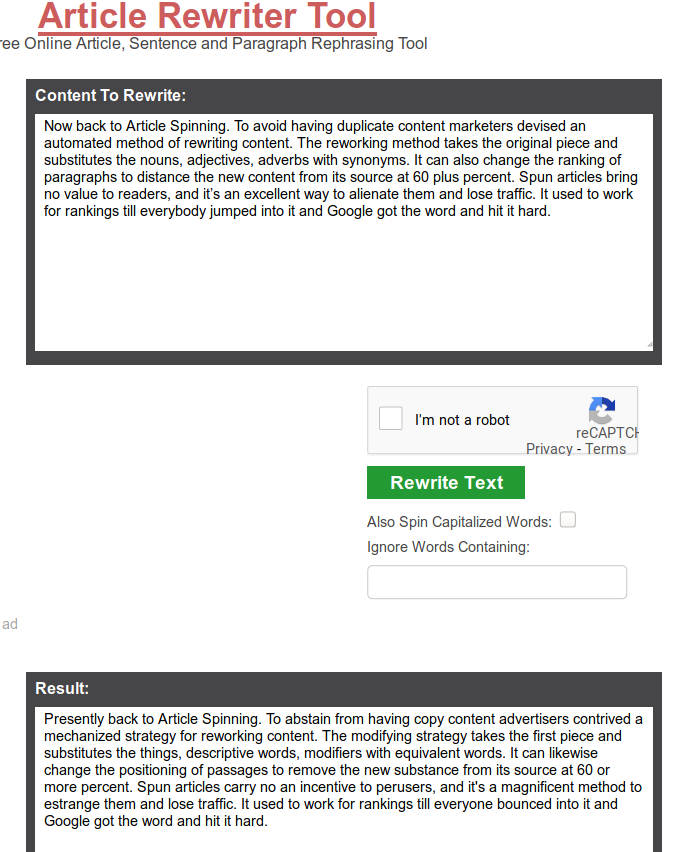
Is Article Spinning spam?
To avoid having duplicate content marketers devised an automated method of rewriting content. The reworking method takes the original piece and substitutes the nouns, adjectives, and adverbs with synonyms. It can also change the ranking of paragraphs to distance the new content from its source at 60 plus percent. Spun articles bring no value to readers, and it’s an excellent way to alienate them and lose traffic. It used to work for rankings till everybody jumped into it and Google got the word and hit it hard.
Software used: The Best Spinner, Word AI, Spin Rewriter, Article Marketing Robot, Deep Spin Poster, Unique Article Wizard, SpinnerChief, Spinbot.
Taken from Articlerewriter.com
How to fix Duplicate content?
Have a content writer prepare your articles, don’t use spinning software. Use one article per campaign, and you’ll be fine. Yes, it will be the same content on all publishers, but it’s better than doing spam. You still have the option to prepare more articles for your campaign and split them amongst publishers.
Link schemes
Google doesn’t like to see webmasters having optimized their inbound links. Google would be happy if everyone did on-site optimization; everything else is manipulation of PageRank. Here I will present briefly advanced link schemes that fall into the black-hat basket. Link schemes are indeed manipulative practices involving inbound and outbound links.
Why are Link schemes spam?
Link schemes that Google penalizes are: buying or selling links that pass PageRank (footer, sidebar, contextual links), guest posting, sponsored posts with links, rewards for giving out links, mutual link exchanges, partner pages, article marketing, and press releases with optimized anchor text in articles, automated link building, non-editorial links, unnatural links, low-quality directory or bookmark site links, low-quality links embedded in widgets, links in the footers or templates, web rings (sites interlinked in a closed network), forum comments with optimized links in the post or signature, blog comments, link farms (irrelevant listings on the same page with lots of outbound links). Google recommends adding a rel=”nofollow” attribute to the ahref tag or redirecting the links to an intermediate page blocked from search engines with a robots.txt file.
Software used: SEnuke TNG, GSA Search Engine Ranker, Xrumer, Internet Business Promoter, Sick Submitter, SheerSEO, Magic Submitter, Free Mass Traffic, Blog Comment Demon, ScrapeBox, Nuclear Link Blaster, Internet Business Promoter, LinkMan.
Online services: TheHoth, Linknami.com, RankWyz.com, Seo-autopilot.eu, Autolinkspro.com (discontinued), Linkautomate.com (discontinued), Infowizardspro.com (discontinued), Link-swapper.com (discontinued).
How to avoid Link schemes?
Don’t buy any type of link (footer, sidebar, contextual). They are not selling links only to you; they are selling to spammers too and sooner or later they get caught. When they do, the publisher and you are busted too. Don’t sell links from your websites unless you’re looking into short-term profit, churn, and burn domains. You’re hurting other peoples’ websites, but you are right to suggest that there’s no ignorance, to begin with here, and everybody gets what he/she deserves. If you are a publisher and you have sponsored posts, add a rel=”nofollow” tag to the links. If you’re writing an article without looking into profit, just link to other pages that you deem useful for your readers without thinking about the type of linking.
Link Exchanges
Link exchanges are part of link schemes that Google penalizes. A link exchange is an agreement between two websites to upload a reciprocal link with both having the goal of ranking better in Google. It was a widespread practice in the past not until Google made it redundant and risky. Link exchange software made it easy to build pages with Resources (link partners). It was very common when webmasters submitted listings to link directories and the latter to ask for a reciprocal link back so they would process faster the listing. Nowadays, established link directories offer only nofollow listings to avoid becoming link farms.
Software used:SEO Powersuite LinkAssistant, Axandra, Koko, Link Exchange Manager, Seoadministrator, Active Link Exchange, Dynamic Link Promoter, Linkmachine.net (discontinued).
Online services: Postlinks.com.
How to avoid Link Exchanges?
It’s an outdated tactic. Stay away, reject all link exchange offers.
Over-optimization
Webmasters trying to rank their sites might over-optimize the image ALT descriptions; It is very easy to abuse the interlinking of pages just by inserting keyword-rich terms between the ahref tags and ahref title=””; Prone to abuse are also HTML heading tags, i.e., multiple H1 tags on a page (H1 stuffing); The misuse of irrelevant keywords (out of context) when one wishes to rank for terms he has no content is an inefficient tactic.
Software used: SEO Powersuite WebSite Auditor, ScreamingFrog, SheerSEO, Web CEO.
How to avoid Over-optimization?
Optimize your content and titles with your visitors in mind. Think about the conversions, not about clicks and rankings. Don’t optimize everything for the search engines; add some randomness, and entropy to avoid looking unnatural.
Guest Posting
When an external source provides the article that gets published on a website this is Guest posting. In itself, the publishing method shouldn’t be at all black. A site with a lot of content has a team of content writers behind it, good writers, and experts on topics. Not every blog belongs to a big media network, and engaging content is hard to produce. Media networks and news sites do it all the time, but they get no penalties.
Why is Guest Posting spam?
Google is cracking down on content for rankings but still, the big guys are left untouched. The head of the Google Spam team, Matt Cutts, announced the hit back in 2014. Guest posting indeed became a shady industry. At least once a day someone contacts me offering to write an article and get a link back. The content is low-quality, and despite Google’s crackdown, those people seem ignorant.
My take is that they don’t care. They are just mediators (arbitrage) between a marketer and a publisher. Both parties will lose from the deal; Google will punish the marketer for getting links from guest posts and the website hosting such types of articles. Only the middlemen win (getting a fee) hence the lack of caution and superficiality in curating the content.
Here are a couple of examples:
“…a blogger outreach service provider and high-quality news publisher through real blogs. Since 2014 I have been in the online marketing field. I have a great resource of high-quality blogs with good PA and DA along with unique visitors. I’m providing high-quality guest post services to all of my clients. It’s also a proven marketing tactic that increases brand awareness and conversions.” This guy has been in business since 2014, yet he missed the signal entirely from Google’s Head of Spam that what he offers is nothing but spam. Then, he offers HQ blogs with authority metrics and unique visitors, but that is never the case. They are probably part of a web ring another link scheme that Google penalizes. Lastly, the HQ content he promises will never happen, plus the brand awareness and conversions don’t come from spammy schemes.
“I have an unrivaled number of existing relationships with high-profile bloggers and journalists, so I am perfectly placed to promote your site’s content and earn those high authority links…” Again here, you will find no high profile bloggers and journalists, no authority from a spam tactic. They even showcase the sites where they allegedly publish without having the consent of the site editors or they offer posts on websites that accept user-generated (free) content.
Software used: Inkybee.com (discontinued).
Online services: Guestpost.com, Blogdash.com, Guestposttracker.com, The Content Facilitator, Guestr.com, Grouphigh.com, Postjoint.com, Myblogguest.com, Uawpro.com, Bloggerlinkup.com, Raventools.com, Authority.builders, Tork Network, Thehoth.com, Clickintelligence.co.uk, Nobs.link, Accessily.com, Goforpost.com, Bloggeroutreach.io, Outreachmama.com, Guestpostengine.com, Linkprospector.citationlabs.com, Contento.marketing, Buzzstream.com, Postrunner (defunct), GuestBlogIt (defunct), Blogsynergy (defunct), Copyforbylines (defunct).
How to fix the Guest posting issue?
Don’t do guest posting. Your content might be good but others’ not. Only a few sites that allow guest posts care about quality content. Most of the time you end up having a medium-quality article on a low-quality publisher who acts as a link farm. If the site authority drops you can’t expect that your paid article will offer you any value, do you?
User-generated spam
Visitors to a site can cause problems when they generate content that violates the search engine guidelines. Remember above that guest post providers may use websites that allow to upload of free content? Their content may raise a red flag about a localized issue in specific public access pages. If the content generally sitewide is low-quality then it affects the whole site. The type of content can be spammy forum accounts and posts, web 2.0 accounts and posts, blog comments, and social network posts (unrelated or malicious links, shady private messages). Usually, all spammy posts and comments require a link back to irrelevant websites.
Software used: ScrapeBox, GSA Search Engine Ranker, Free Mass Traffic, Blog Comment Demon, Blog Comment Poster, KomentBox, Nuclear Link Blaster, Sick Submitter, Fastblogfinder, Magic Submitter, Blogcommentor, Blog Comment Poster.
Online services: Fiverr.com, Freelancer.com, Guru.com, Microworkers.com, Crowdsearch.com, Quickregister.net, Postlinks.com, Uawpro.com, Magenet.com, Linksmanagement.com, RankWyz.com, Bulkcomments.net, FCSNetworker.com, Alexa backlinks, SmartComment.com, Commentanywhere (defunct).
How to fix the User-generated spam?
Don’t do guest posting. Monitor your forum posts and ban those accounts that offer no value. Web 2.0 administrators can’t do much as the sheer amount of submitted content is overwhelming. They either allow user-generated content or ban it. Bloggers can limit the number of comments per post, approve them manually, and add the rel=”nofollow” tag to external links. Social networks can do better as they have the resources allowing them to hire human curators.
Let a pro handle the details
Cloaking
When a website offers different results to human users and search engines it deceives both parties to achieve better rankings. It acts similar to sneaky redirects and has a common aim, but the affected parties here are different. Cloaking serves different sets of content to humans i.e., images or Flash and text to search engines or presents crawlable elements when the User-agent is a search engine. Not to confuse cloaking with accessibility options. For example, when the website technology is Flash, search engines do not crawl it and there are ways to make them understand what the site is about.
How to fix the Cloaking issue?
Offer the same content to visitors and the search engines. If you run a Flash site make sure the search engines have descriptive text as a guide.
Bait and Switch
It’s a false marketing (illegal) technique when a page ranks for a specific keyword set, and then the spammer changes it to another topic. The page keeps the link authority but now serves a different purpose. The line is thin (Grey-hat) between this tactic and the use of old domains that change their owner but keep their topic/link authority. The old domain gets new content or 301 is redirected to a new domain/page. The topic can be the same or altered, but surely, the location (domain) is not the same. Therefore, even old domains often fall into the ‘Bait and Switch’ bucket.
A similar tactic is Clickbait, where the heading does not match the content on-page. The deception aims solely at clicks and uses eye-catching titles. When users click to find content different than expected, they quickly leave increasing the bounce rate (bad for ranking).
How to fix the Bait and Switch issue?
Don’t change the topic of your pages ever. If you buy an old domain, try to build it around its old theme, else if you have to buy it, SEO might not be a traffic contributor. It might have its readership visiting it directly or via affiliates, but search engine traffic might be compromised.
Referrer Spam
Referrer spam tries to game the rankings by producing statistical data. Automated bots (software) hit the target site generating fake traffic and getting a link back from the public statistical report page.
Software used: GSA Search Engine Ranker.
How to Fix Referrer Spam?
It’s an old method 100% spam, drop it.
Pinging
Pinging is a way to let the search engines know that you have uploaded new content or updated existing one. There are different ways to ping the engines. Online or desktop tools use the page URL and sometimes allow the insertion of relevant keywords. Content management scripts like WordPress have a way to notify of the changes and by default use the service http://rpc.pingomatic.com under the Settings / Writing / Update Services section.
It’s all about content indexing. New or low-quality websites have a hard time indexing their content. Google will crawl the content, but it may take days or weeks to index it (my site indexes new content within minutes).
Why is Pinging spam?
Pinging services send automated notifications to search engines. SEOs use pinging to make search engines notice their backlinks. Pinging a couple of backlinks does not harm, but sending bulk pings, i.e., 50 or more links raises the spam flag. In the past, marketers used RSS feed services to group their backlinks into a single RSS feed and ping it. It’s all about quality. Good content does not need pinging.
Software used: SEnuke TNG, GSA Search Engine Ranker, Xrumer, Free Mass Traffic, Backlink Samurai, Index Nuke, Backlink Beast, GSA SEO Indexer, ScrapeBox, Sick Submitter.
Online services: Pingomatic.com, Pingler.com, Rssmix.com, Pingfarm.com, PingOrange.com, Feedshark.brainbliss.com, Onehourindexing.co, Linklicious.co, Backlinks Indexer.
How to Fix Ping Spam
Don’t do extensive or intensive pinging. If you have some new backlinks either let the search engines find them on their own or break them into small chunks and drip-feed them. Just make sure you don’t repeat the process. Eventually, they will be found. If they are not indexed, it means they are not good quality, so just leave them.
Trackbacks
Trackback is an old method of communication between blogs still in place. When an article on a blog links to a blog page outside the own blog it sends a ping and the receiver blog sees it as a trackback (link from page X). The receiver has the option to approve and publish the trackback giving a backlink to the source. Spammers abused the trackbacks by trying to influence the rankings. Trackbacks became nofollow but still, the spammers use it although reduced. Spammers also abused trackbacks by getting bloggers to visit their pages.
Software used: ScrapeBox, GSA Search Engine Ranker, Trackback Ninja, Trackbackspeed.
How to fix the issue
Don’t do any trackbacks; they offer no value whatsoever. Leave them for the spammers.
Link Directories
It was a common practice in the past to submit a new site to link directories. Most of them were free, and some paid. Today Google has cracked down on link directories as sources of spam. Even so, paid directories advertise the placements as a good thing to have from a high-quality, human-curated directory. But those paid placements are bought links something that violates the search engine guidelines.
Software used: GSA Search Engine Ranker, Fast Directory Submitter, Free Mass Traffic, Submiteaze (defunct?), Blog Blaster, Sick Submitter, Internet Business Promoter, Dynamic Submission, SheerSEO, Web CEO, SubmitWolf.
Online services: Quickregister.net.
Taken from Submiteaze
How to avoid the Link Directories spam
If you need to submit your site to link directories, then do a few of them that are close to your location. It won’t do anything to get links from remote or outlandish places. Don’t overdo it, pick the closer ones and think that someone may see your listing and click to visit your site. Don’t think about the links, even a “not clean” (redirect) will do.
Social Bookmarking
Users submitted (bookmarked) their pages in tens of thousands of websites built on small scripts (see below) with vulnerabilities. They called it social because it was user-generated content from logged-in users and other users could tag the submission. Spammers abused it, and editors didn’t pay attention to low-quality content. Google hit the social bookmarking sites because they influenced the rankings. Yes, it did have an impact, but now it’s spam. Hence big websites (below) have changed the submission process and switched to other content, i.e., images imitating Instagram, videos, or copying Twitter.
Online services: Reddit.com, Slashdot.org, BibSonomy.org, Diigo.com, Pearltrees.com, Pinterest.com, SiteBar.org, Weheartit.com, Plurk.com, Pinboard.in.
Defunct services: Digg (live but not accepting social bookmarks anymore), Bookmarksync, Clipmarks, Del.icio.us, Faves, Furl, StumbleUpon, Newsvine, Xmarks, Socialmonkee.com, Onlywire.com, SocialMarker.com.
Software used: SEnuke TNG, GSA Search Engine Ranker, Bookmarking Demon, Imautomator, SocialAdr, Backlink Beast, Sick Submitter, BookmarkWiz, SocialRobot, Social Bookmarks Submitter.
How to fix the Social Bookmarking spam
Think of social bookmarks as a way of generating traffic, not backlinks. With that in mind, it’s easy to figure out how many and to which you should submit your page. My point is, do only a few (max 10) knowing that you only do it for the traffic. It won’t have any effect on your rankings.
Press Releases
The emergence of many websites allowing to submit press releases, picked up by media outlets, and the effect they had on rankings led to abuse. Informing the press on a company event became distant. The content was low-quality and not company news, the press release had a single end, getting as many backlinks. No journalists would pick up the story; no media outlets would publish a piece.
Google soon caught up with the abuse and penalized press release websites and websites getting the backlinks. That led to a significant reduction of the tactic with the PR websites allowing only nofollow backlinks at the author’s box if any.
Software used: Magic Submitter, SEnuke TNG, GSA Search Engine Ranker, Backlink Beast, PitchEngine.
Online Services: Newswire.com, PR.com, Prweb.com, Prnewswire.com, openPR.com, WebWire.com, PRunderground.com, Prezly.com, Prgloo.com, West.com, Emailwire.com, 1888pressrelease.com, Marketpressrelease.com, Express-press-release.net, Prurgent.com, Pr-inside.com, prMac.com, Accesswire.com, PRLog.org, Businesswire.com, Newswire.com, PressPage.com, Prowly.com, Free-press-release.com, Send2press.com, 24-7pressrelease.com, Prnews.io, Pressat.co.uk.
How to avoid spamming with Press Releases
If you need to get the attention of the media to your story, do a press release choosing the best media outlets. If your story is noteworthy, some journalists will pick it up, and maybe you get the spotlight by giving an interview. If you aim merely at getting backlinks don’t bother. Note that sending a press release to media outlets is a costly service. Anything less is spam.
Whois databases
Whois Databases are websites that list domain names with a description, the site meta tags, headings, code technology, and a couple of points to optimize. The gain is an immediate backlink. A few of them won’t hurt your site. The issue is when spamming with hundreds or thousands of Whois submissions.
Software used: BacklinkSpeed, GSA Search Engine Ranker.
How to fix the issue
Do only a few of them if you need them.
Article Directories
Article marketing is spam for the same reasons as guest posting is. There are many similarities between the two. In article marketing, there are two aspects. The first is the large quantities of articles disseminated across blog networks/news sites with the sole purpose of gaming the rankings. The second is the now almost defunct article directories with practically no curators.
The idea was great in theory. If a company wrote a great article, it could become viral and send lots of traffic to their landing pages. The practice has shown that no article ever attracted readers or sent visitors, but there was only abuse. An article directory campaign could easily amount 300 Article Directories. An article marketing campaign usually goes below that number, from 25 to 100 articles. Then, there was the auto-generated content that produced low-quality articles and the article directories soon became link farms. Good articles are only a few and places to disseminate them even fewer.
Software used:Magic Submitter, SEnuke TNG, GSA Search Engine Ranker, Backlink Beast, Buildmyrank, Sick Submitter, Article Marketing Robot, Article Submission Helper, Article Marketing Suite, Article Kevo, Automatic Article Submitter.
Online services: Quickregister.net, SeedingUp.com
Taken from Ezinearticles.com
How to fix the issue
Focus on your readers. If you go for the backlinks and rankings you will lose as everybody does that, the competition is harsh, and Google swings its bat. Focus on what you write, and for whom you write it, and find places with traffic to publish it.
Reviews
Few product reviews are original and sincere. There is a lot of manipulation of product or service reviews because the market share is limited. Two aspects here: One is where those reviews show up and do they influence the buyers? Second, do those reviews affect the website/product rankings?
Incentivized reviews you can have in many ways. A buyer gets a discount for the next time he buys a product if he leaves a positive review on his last order. A traveler gets free stuff or a discount if he leaves a positive review at TripAdvisor, or GoogleMyBusiness of his accommodation or travel service during his stay. A company buys X number of positive reviews, for its mobile app on the Google App Store or its money transfer service, etc. There are incidents with fake reviews on TripAdvisor, Amazon, etc. TripAdvisor has caught 75 paid reviewers who were selling “user” reviews to businesses listed on the site and claims to have stopped 1 million fake reviews from reaching the site. Additionally, TripAdvisor has in place a ranking penalty that demotes businesses (34,643 so far) who try to game their rankings with fake reviews. Fake TripAdvisor reviews can also be of a different kind of spam like the incident described in the SUN newspaper of a rundown pub turned into houses but still getting reviews five years after it shut.
Fake reviews by manipulation of rating stars and comments on your site will make you a target for rankings manipulation. My take is that the review systems have flaws, and if they still affect the rankings, Google should stop this money-scheme industry.
Software used: SheerSEO.
Online services: Trustpilot.com (claims of fake reviews and money schemes see here https://trustedcompanyreviews.com/review/trustpilot-com/), Reviews.io (they claim that Trustpilot.com employees have left some reviews on their site), G2.com, Testfreaks.com, Trustedcompanyreviews.com, Unitedservicers.com, Reputationloop.com, Repcheckup.com, Myreviewninja.com, Yext.com, Respondelligent.com, Localclarity.com, more here: capterra.com/review-management-software.
Taken from Trustpilot
How to avoid spamming with Reviews
Ask for genuine reviews and help the customers leave them effortlessly if you have a review system on your site. Don’t ever offer incentives in return for positive reviews. Don’t use online services that ask you for money. Use only services that let you leave free and verified reviews. Don’t manipulate your business reviews by any means.
Paid Advertorials
An advertorial is an advertisement on a website and as such is paid content. Advertorials target specific audience segments, offer more content than standard ads and companies purchase the ad space. All links within advertorials pages are paid content and as such, breach the search engine guidelines.
How to avoid a Paid Advertorial penalty
Don’t advertise your company in advertorials that don’t offer the nofollow tag. If you are a publisher, be sure to insert the nofollow tag to all advertorials’ links to show that this is a sponsored post and avoid penalties.
Pages with Malicious Behavior
Pages with malicious behavior have content that behaves unexpectedly, downloads, or executes unsafe files on a user’s computer without their consent. Trick users into clicking content that’s not supposed to be there; inject popups; swap ads with different ones; install software that contains malware, adware, and trojans; download unwanted files; hijack the browser homepage and preferences.
How to Avoid Pages with Malicious Behavior
Get yourself a good antivirus, be careful which pages you visit, don’t click yes on every popup, don’t click on suspicious ads, and don’t download any files. Use Firefox, and Chrome browsers with enhanced security and even check to install extra security plugins against popups and malware.
Parasite Hosting
Parasite or parasitic hosting (2007) hijacks a server (usually .edu domains) and hosts there a sub-domain, a sub-page, a blog, wiki, or forum with irrelevant content compared to the root domain. Its main goal is ad revenue from ad placements and/or better rankings by injecting a host of links and stuffing keywords thus benefiting from the root domain’s authority.
Online services: siteguarding.com
How to avoid falling victim to Parasite-hosting
Monitor your web server for unwanted content. Google Webmaster Tools gives you a report with the status of your pages. There are online tools to help you with scanning for outbound links i.e., siteguarding.com.
Private Blog Networks (PBN)
Private Blog Networks are groups of websites or blogs with the sole purpose of gaming Google rankings. It used to work in the past as a source of generating topic relevancy with a host of backlinks. Nowadays, Google hits the biggest networks and discovers quickly private ones. PBNs offered a lot of flexibility to change the topic and manipulate the content in favor of a new client. PBNs exploit the authority of expired domains (link juice) but remember the issue with Bait and Switch above? Old domains don’t pass the authority and link juice they used to anymore thanks to Google spam measures. It was a major topic back in the day when Google deindexed big networks with millions of pages and thousands of clients. It was a big topic back in the day when Google deindexed big networks with millions of pages and thousands of clients.
Software used: PBN Builder, PBN Tester Pro.
Online services: Link Authority, RankWyz.com, FightBackNetwork.com, Pbndomains.net, Pbnlab.com, Seo-autopilot.eu.
How to avoid a PBN penalty
Don’t build PBNs. Google will find out, or a competitor will submit a spam report against you, and you will burn any domains connected to the network. Don’t buy links from other private or public PBNs as they are riskier than your own. Everybody buys links from those PBNs, so they get burned fast.
Google Bombing
Spammers build a page and try to rank it as number one in the SERPs for a particular search phrase by building a host of anchor text-optimized backlinks to the page. Then users who run these searches find unwanted, surprising, expletive, insulting, disparaging, and sometimes hilarious results. Google changed parts of its algorithm in 2007, making it harder for spammers to launch Google bombs. A famous example of Google bombing is the one with Mitt Romney, giving out image results for the phrase ‘completely wrong.’ When searching in Google for the phrase “find Chuck Norris” and hitting the “I’m lucky button” it comes up the result “Google won’t search for Chuck Norris because it knows you don’t find Chuck Norris, he finds you.”; George W. Bush was ranking with his biography page on the White House website when searching for ‘miserable failure.’
How to fix the issue
If a spammer launches a negative result against someone, then there are two ways to react: a) submit a report to Google and wait enough time for them to act on it; b) hire an SEO to eliminate the negative results.
Negative SEO
Negative SEO is not about reporting your competitors to get them penalized, but it’s about creating a false reality with their link profiles. It’s the effort to make a competitor’s link profile show spammy and receive punitive action from the search engine algorithms. To do that, competitors hire a black-hat person who goes out and bombs the target domain with thousands of spammy links, i.e., gambling, adult content, marijuana, etc. Another option is to harm by buying thousands of spammy links from sites like Fiverr.com and bombarding the target domain. Eventually, it will raise a red flag in Google’s computation systems.
Software used: Xrumer, SEnuke TNG, GSA Search Engine Ranker, ScrapeBox.
Online services: Monitorbacklinks.com, SEMrush.com, Raventools.com, Fiverr.com, Freelancer.com, and black-hat forums.
How to fix the issue
The only option is to hire a white-hat SEO and start cleaning the spammy by disavowing links and doing hand-picked interventions. It will take some months, but it will sanitize the slammed domain.
Thin Affiliates
Typically, affiliate websites focus on fast profits and don’t care about content originality. They will either scrape content or copy and paste product descriptions without altering a byte. They might also replicate content and templates across multiple domains or languages. Google knows that these sites are made precariously and don’t offer enough added-value content. If shown in search results, they would return the same descriptions and create a bad user experience. They call them “thin affiliate” websites and gladly cut down their traffic.
Examples of thin affiliates are pages with product affiliate links where the product descriptions and reviews are copied directly from the original merchant; and sites with mostly affiliation pages without original content. Thin affiliate sites will see demotion in their rankings or be thrown out of the index.
Online services: Jam.jrox.com.
How to avoid the Thin Affiliates issue
Don’t just republish content from the original merchant. Offer unique product reviews, ratings, navigation of products or categories, and product comparisons. Enrich your affiliate site with content to reduce the number of affiliate pages and differentiate from the flock. Add value for the visitors; otherwise, they will visit the original merchant directly. March your affiliate program to your intended audience; you will rank better. Build community among your users to help your email list and retain your readership. Ideas that could help are discussion forums, user reviews, and blogs. Update your content regularly; this way, Google will find fresh content and will increase your readers’ engagement.
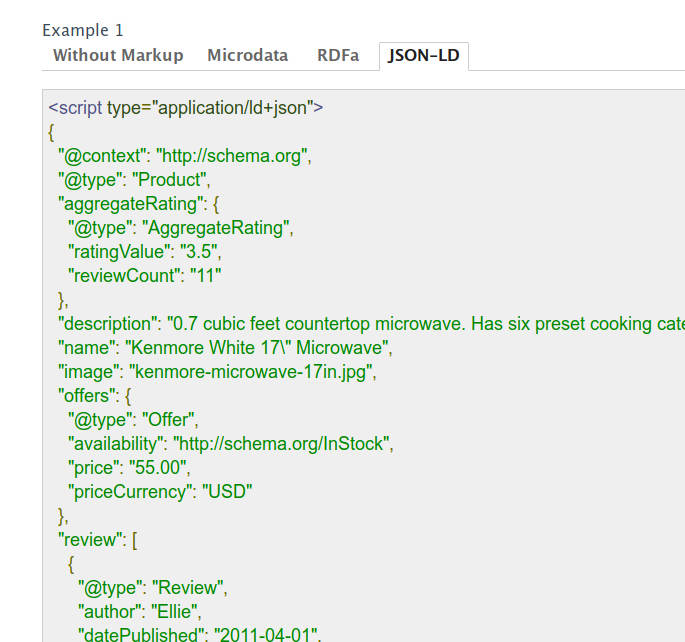
Rich Snippet Markup
Structured markup data defines the appearance of your pages in the search results, and in that sense, it’s legitimate. It’s the best way to contain information, benefit the click-through rate, make useful content more visible, and reduce bounce-rate. Rich snippets show up in the results of products, music, videos, restaurants, recipes, businesses, events, people, and authors. Spammers create deceiving, irrelevant, and misleading rich snippets. The most common examples are the reviews and ratings showing false ratings, stars, or having no system for leaving reviews.
Let a pro handle the details
How to fix the issue
Use rich snippets that match your page content. Don’t manipulate reviews and ratings. Don’t insert irrelevant or false information.
Widgets
The idea here was to create a widget and share it with webmasters so they might place it on their sites and get a link back. Widgeteasy.com was a free service that helped with widget creation, while a paid one was Widgetbox.com. The widget creation was smooth, and you would get the code to paste on your site. Another option was to submit your widget to the widget directories and get a backlink.
Online services: Widgetbox (now defunct), Widgeteasy (service discontinued).
How to fix the issue
The method is old and spammy, don’t use it.
Toxic Sites – Bad Neighborhood
Toxic sites are part of link schemes, and if you get links from such bad reputation sites, you have an issue. It may be a toxic topic or the site’s affiliations that create a problem. In both cases, it harms. Google has devised a way of demoting toxic backlinks, but it’s not perfect, and you can’t be too careful.
How to fix the issue
Monitor and review your backlinks regularly. Take down or disavow toxic backlinks.
Blog Reviews
In the old days! there was a method of review swapping, and those reviews were not genuine but made for profit. Exchanging blog reviews offered also to exchange links, another downside.
How to fix the issue
It’s unnatural, manipulation, and deception. Don’t engage in it.
Automated Google Queries?
Spammers can send automated, or semi-automated Google queries to manipulate the search rankings by inflating the number of searches for a specific keyword. The idea is that when real (questionable) people search for a particular phrase and click on your result, Google will figure out your page is the most relevant for the search phrase. They are offering even the option to negative click (click and leave immediately, inflating the bounce rate) on your competitors to take them out.
Online services: Serpclix.com, Crowdsearch.me, Microworkers.com.
How to fix the issue
Don’t use services that produce unnatural Google queries and manipulate the rankings. All unorthodox methods get busted.
Wikis/.EDU Domains/.GOV Domains/Wikipedia Hijacking
Spammers use Parasite Hosting methods to hijack pages on high-authority wikis, .Edu, and.Gov sites. The .Edu domains are the most favorable as the administrators can’t monitor thousands of pages, universities allow freedom of speech, and users have more control than in other setups. The method is uploading relevant content and placing backlinks to manipulate the rankings. They also try to create articles on Wikipedia or insert their backlinks in the References section.
Software used: GSA Search Engine Ranker, Link Hijack, Wiki Ranker, WikiRobot.
How to fix the issue
Wikis are not influential to rankings; you’ll waste your time and risk. On the other hand, .Edu and .Gov domains carry high authority but hijacking their pages is illegal.
Cybersquatting – Domain Squatting
Spammers exploit typos and abuse country TLDs to create domains that look similar to famous brands. It’s an illegal practice, copyright infringement, and cybercrime.
How to fix the issue
Report the spammer to Google and request them to take down the domain for illegal practice, and copyright infringement.
Domain – Page Hijacking
To hijack a domain is to steal it from its owner. Usually, a former webmaster who has still access to the registrar dashboard can change the registration details and redirect visitors to PPC ads. The owner loses revenue, traffic, staff, and users’ email accounts, branding, and all advertisement material in connection to the stolen website. The hijacker may create an identical webpage to phish passwords, and private information, engage in spamming, and inflict other damages to third parties while still holding the previous owner accountable.
There are affiliate marketers who hijack squeeze pages to insert their affiliate links. And they are so proud that they make videos to brag about it. A squeeze page costs below $18, but they don’t just steal the template. What they do is scrape the whole page/site, including copyrighted images, texts, CSS, and JS files. What they then do is use an editor to insert their affiliate links in the CTAs. Besides infringing copyright laws, they also create duplicate copies of the stolen page. So, they harm the owner twice plus harm their marketing efforts in organic search. Of course, these lazy spammers would not make an effort to work the SEO and only engage in paid ads.
How to fix the issue
Keep all your registration information and access details confidential. Don’t share them with anybody even if you are not proficient in managing your domain and server. With webpage scraping tools, there’s nothing to do to avoid scraping the content. What you can do, is search in Google for content chunks or code chunks from your page and follow takedown procedures (contact DMCA, Google, Legal, ISP).
Buying Likes and Followers
Spammers buy likes, followers, and retweets, to influence how their content shows up in Google search and social networks’ feeds. They can promote their pages or their Facebook Fan page, their Twitter account, and their Instagram account. The practice is illegal, breaches user agreements and when found can take down your pages, and lose your business accounts.
There is no way your pages will rank better if you have more FB likes and retweets. The social networks are aware of the manipulation and will not allow your content to surface. Instagram has eliminated the likes on user posts. Facebook has changed its news feed demoting business pages. Twitter takes down accounts every day.
Software used: Followadder, SocialCaptain, Instagrost, Instaliker, Combin.
Online services: Tweepi.com, LikesTool.com, Uawpro.com, Viralcontentbee.com, Feedmefollowers.com, Hitspeeds.com, Buymorelikes.com, Audiencegain.com, Socialshop.co, Mediamister.com, Socialshark.com.
How to fix the issue
Save your money and don’t buy likes, retweets, or followers. Focus on creating more engaging, genuine content.
Mirror sites
Spammers duplicate the content of a site creating a mirror site or replica. This way, they hope to increase their ranking. Replicas in server management are used to help with network traffic when the original site generates too much traffic for a single server to support. Mirror sites are used for overseas audiences to access the content faster. It is problematic when a site has an exact copy or more copies in other locations visible to the search engines. It is duplicate content and a spam practice.
How to fix the issue
Never use replicas or mirror sites. If you have to, you need to block them from indexing in the search engines.
Traffic Boosters
What these sites do is boost the traffic of a page artificially. The myth is that when you have the traffic you also enjoy higher rankings and make sales. The problem is that this traffic is unnatural, autorefresh bots use proxies to appear as though they come from around the world, and that raises spam flags. If you have bots visiting your site, you cannot make sales. Unnatural traffic doesn’t boost your rankings. The only thing you can get out of it is a Google penalty or deindexation. On the other hand, traffic exchanges are real people visiting your site, direct traffic, but they’re not interested in what you offer. Therefore, the downside is that you will increase your bounce rate and lower your conversion rate. The only profitable but illegal aspect I can see is that you inflate your traffic when you are selling page views to advertisers.
Software used: TrafficBotPro, One Million Clicks, Website Auto Traffic Generator, Traffic Magnet, QoS Traffic Generator (Daytona), Active WebTraffic.
Online services: Babylontraffic.com, Hitspeeds.com, Traffboost.net, Trafficprogrammer.com, Boostvisits.com (discontinued).
How to fix the issue
Don’t use unnatural traffic, like bots or traffic exchanges. It won’t offer you the results you expect, might raise spam flags, and certainly won’t affect your rankings positively.
Microworkers
Hiring workers to do small tasks is spam when they manipulate your website traffic and reviews or inflate the likes, views, and votes of your posts either on-site or on social networks.
Online services: Microworkers.com, Freelancer.com, Fiverr.com.
How to fix the issue
Don’t manipulate traffic, reviews, likes, views, votes. It’s spam, and you will have your website deindexed and lose your social accounts.
Fake Video Views
Spammers inflate video views on YouTube to have their videos rank on the first page of YouTube search. This practice violates the YouTube user terms and risks terminating the account. Fake views devised to appear that they are real people viewing your video from across the world, but you won’t measure any clicks to your pages. It doesn’t have a significant impact on ranking a video in YouTube search (waste of money).
Online services: Microworkers.com, Freelancer.com, Fiverr.com, Hgfollowers.com, Smbuys.com, Famoustube.net, Fastsocialz.com.
How to fix the issue
Don’t use services that inflate your video views. It’s against the user agreement, your video and account might be taken down, and you’re wasting your money in spammy actions.
Cookie Stuffing – Dropping
Spammers drop cookies in scripts, pop-ups, toolbars, and images. The cookies are stored in the visitors’ computers, and when they visit a site that pays for advertising, the spammer receives a fee.
How to fix the issue
Dropping cookies is an illegal practice. Users can protect themselves by installing privacy plugins that limit the use of cookies.
Email Marketing
Technically it’s not SEO but I will include it in my list as it’s spam. Any unsolicited email, sent in bulk to a list of people is spam. Spammers sell lists of email addresses that they advertise as having given their consent to be on the list, but that’s never true. According to Canada’s Anti-Spam Legislation (CASL), spammers pay $1-10M per violation, and the CAN-SPAM Act of 2003 spammers fines with $11,000 for each email address on their list. The CAN-SPAM Act of 2003 requires non-deceptive headers, From names, reply-to addresses, or subject lines; an unsubscribe link to work for at least 30 days after sending and a physical mailing address.
Spam filters and firewalls don’t catch every spam message out there, and new methods come up every day. Ignorant spammers are very hard to detect and prevent. Non-opted-in receivers of spam can send an abuse report to SenderBase. Senderbase is the world’s largest email monitoring network. Once a report arrives your sender IP is blacklisted. For many years now I have worked with SpamCop.net. Every gatekeeper has now your blacklisted IP and your reputation score is down. Even if you switch email servers, they have you under their lens because they work with content-based spam filters. Abuse reports arrive at the ISP, and when they reach a threshold, the ISP sends an automated warning message to the sender and can suspend the account. Users can click the report spam button in their email management software or web interface, and of course, can submit manual reports to the ISP and anti-spam organizations.
Software used: Blast4traffic.com.
Online services: SpamCop.net, Stopforumspam.com, Hubspot, Mailchimp, AWeber, GetResponse, Ontraport, Constant Contact, Drip, SendinBlue, ConvertKit, ActiveCampaign, SendX, Benchmark, Sendlane, iContact.
How to avoid email spam
Don’t purchase, rent, or scrape email lists. Only include opted-in subscribers to your lists. Comply with the regional requirements before sending email messages. Non-opted-in subscribers will increase the bounce rate, and you may even have legal ramifications. Ask for permission even from your already customers and contacts. Customers who purchase from your store should also opt-in to be on your list. Give details on what people should expect when they join your list (frequency, type of promotional material, updates, offers). Regularly update your mailing lists as old subscriptions may lead to spam complaints. Offer a visible unsubscribe link.
Here is a copy of an unsolicited email I received offering me to buy a list of subscribers:
from: rob…@gmail.com
Hi,
I hope you are doing well. We come up with the email lists in best price. Here is an exceptional offers listed below.
1. Hospitals Industry – 8000 c-level contacts (Owner, President, CEO, CFO, Etc.) are just $300 only.
2. Gasoline and Oil Refineries Industry – 8,000 c-level contacts are just 300 only.
3. Bank Industry – 10,000-level contacts are just $350 only.
4. Hotels, Motels and Lodging Industry – 7,500 C-level contacts are just $300 only.
5. Facilities Management and Maintenance Industry – 8,000 c-level contacts are just $300 only.
6. Architecture, Engineering and Design Industry – 8,000 c-level contacts are just $300 only.
7. Construction and Remodeling Industry – 8,000 c-level contacts are just $300 only.
8. Aerospace and Defense Manufacturing Industry – 6,500 c-level contacts are just 240 only.
9. Retail Industry – 3500 c-level contacts are just $150 only.
10. Warehousing and Storage Industry – 2000 c-level l contacts are just $100 only.
11. Textiles, Apparel and Accessories Manufacturing Industry – 3000 c-level contacts are just $100 only.
12. Medical Supplies and Equipment Industry – 1500 c-level contacts are just $70 only.
13. Residential and Long-Term Care Facilities Industry – 5000 c-level contacts are just $180 only.
14. Restaurants Industry – 10,000 c-level contacts are just $400 only
15. Furniture Stores Industry – 2,000 c-level contacts are just $100 only.
16. Hardware and Building Material Dealers Industry – 2,000 c-level contacts are just $100 only.
17. Dentist Job Title list – 2,000 contacts are just $100 only.
18. Nurse Practitioner Job Title list – 5,000 contacts are just $200 only.
19. Colleges and Universities facility managers Job Title list -7,000 contacts are just $240 only
Please let me know if you are interested in any above lists.I can send you few samples which is of no cost. Price will be negotiable if you are purchasing all the above lists.
Look forward to hear from you. I appreciate your time and patience in advance. Thank you.
Best Regards,
Robert
Mass Search Engine Submission
In the early days of the internet, there were no search engine bots and indexing. People used to submit their websites to the search engines to be found. The practice has endured for ignorant webmasters (or maybe not so after all) who think it will do well submitting their site from 20 to 20,000 search engines (doubt it there are so many). Manual submission to the few big ones is OK. Mass submission to hundreds is spam.
Software used: Internet Business Promoter, Web CEO, SubmitWolf, Dynamic Submission.
Online services: Entireweb.com, Freewebsubmission.com, Addme.com, Submitexpress.com, Addurl.nu.
How to fix the issue
Don’t use mass submitters. It’s spam practice, and we are not in 2007 anymore. The significant search engines will know where to find your site and the others copy the results from the big ones.
Fake Awards (Nettyawards.com and Thenettyawards.com)
A bunch of Indian scammers with flip-flops from Mumbai, Jaipur and Uttar Pradesh send an unsolicited email that your business has been “nominated” and you should act fast (the typical marketing principle of urgency) because they need to meet their deadline to “finalize the nominations/press coverage list”. The downside is this fake nomination has a $495 fee (the scammers can live for 2-3 months on that money).
Now if you’re smart enough and do a little digging you will find these are known scammers who are already blacklisted and I doubt the victims will ever get even a link after payment. Their names show that they are Caucasian ladies with fake identities and pictures. For all I know, the imposters could very possible be males named Vikrahm, Ajay, or Sanjay.
https://cleantalk.org/blacklists/sarah.levine@thenettyawards.com
https://cleantalk.org/blacklists/eva.cohen@nettyawards.com
This guy has written an article about their scheme
Don’t fall for it.
How to Fight the Fake Awards Scheme
Blacklist their domains, and emails on scam ratings’ websites e.g. https://www.scamadviser.com/ etc.
How to Fight Comment Spam
Spammers abuse comment systems with scripts and software to generate and post spam. A common way to detect spam is the irrelevant comments and the link or links to the sites the spammer promotes. The disadvantages of comment spam, when published on your website, are low-quality content that affects the whole site’s rankings; bad user experience; high server loads; demotion or deindexation of pages with user-generated spam; and content leading to malicious websites.
Software used: SEnuke TNG, GSA Search Engine Ranker, Xrumer, Internet Business Promoter, Sick Submitter, SheerSEO, Magic Submitter, Free Mass Traffic, Blog Comment Demon, ScrapeBox, Nuclear Link Blaster, Internet Business Promoter, LinkMan.
Online services: TheHoth, Linknami.com, Autolinkspro.com (discontinued), Linkautomate.com (discontinued), Infowizardspro.com (discontinued), Link-swapper.com (discontinued).
Comments need time for moderation; otherwise, they tend to create long pages full of spam. Guestbooks and comments are a thing to consider if you need them. Turn on comment moderation, this way you will review each comment before appearing on your site. Turn on email validation at the new account creation and any email filters available. Use anti-spam tools for account creation like CAPTCHA and blacklists. Enable the use of rel=”nofollow” for every dropped link in the comments. Use filters like trusted content to block suspicious content from showing up; you don’t know what everybody may drop. Block access to untrusted pages with meta tags in the header or use the robots.txt (Disallow:/pathtountrustedpage/untrustedpage). Use user reputation systems to allow your users to help identify spammers.
How to Report Spam
You can report spam sites, remove content from Google, etc.
– Report sites that buy or sell links (paid links);
– Report sites that distribute malware;
– Report rich snippets manipulation;
– Report phishing sites;
– Report copyright issues and take down sites from Google;
– Remove personal information from Google search;
– Remove outdated content from Google search;
– Remove the “This site may be hacked” message: Request a review in the Security Issues section in the Search Console when your entire website is clean and secure.
Let a pro handle the details
Photo by Keagan Henman on Unsplash